As the Map of the Monroe Doctrine takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The Monroe Doctrine, a cornerstone of US foreign policy since 1823, has shaped the course of history in the Americas. This detailed map and accompanying analysis provide a comprehensive overview of its key provisions, impact on Latin America, and evolution over time.
Historical Context
The Monroe Doctrine, proclaimed by US President James Monroe in 1823, emerged amid the backdrop of European powers seeking to re-establish colonies in the Americas following the collapse of Spanish rule.
Driven by concerns over the potential threats posed by European intervention, the United States aimed to safeguard its interests and assert its influence in the Western Hemisphere.
Motivations and Objectives, Map of the monroe doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was primarily motivated by the desire to prevent further European colonization and protect the newly independent nations in the Americas.
- To deter European powers from interfering in the affairs of the Western Hemisphere.
- To promote the principle of non-intervention and respect for the sovereignty of independent nations.
- To establish the United States as the dominant power in the region and expand its sphere of influence.
Key Provisions
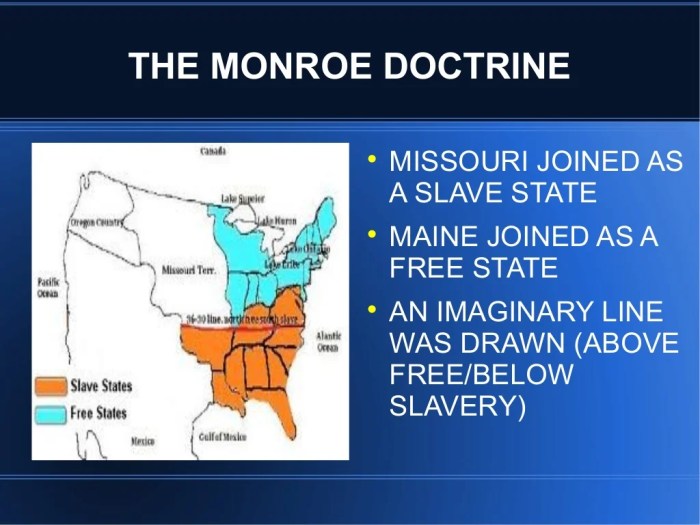
The Monroe Doctrine Artikeld two main provisions that significantly influenced US foreign policy:
1. European Non-Intervention in the Americas: The United States declared that any attempt by European powers to colonize or interfere in the affairs of independent nations in the Americas would be considered an act of aggression against the United States.
2. US Role as Protector of the Americas: The United States asserted its right to intervene in the affairs of Latin American nations if it deemed such intervention necessary to protect its own interests or the stability of the region.
Impact on Latin America: Map Of The Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine had a profound impact on Latin American nations, both positive and negative. On the one hand, it protected them from European colonization and intervention. On the other hand, it also limited their sovereignty and made them dependent on the United States.
Protection from European Colonization and Intervention
The Monroe Doctrine was a clear warning to European powers that the United States would not tolerate any further colonization or intervention in the Americas. This had a significant impact on Latin American nations, as it prevented them from being drawn into the conflicts between European powers and helped to preserve their independence.
Limitation of Sovereignty
While the Monroe Doctrine protected Latin American nations from European colonization and intervention, it also limited their sovereignty. The United States often used the doctrine to justify its own intervention in Latin America, and this led to a number of conflicts between the United States and Latin American nations.
Dependency on the United States
The Monroe Doctrine also made Latin American nations dependent on the United States. The United States was the only power that could protect them from European intervention, and this led to a situation where Latin American nations often looked to the United States for guidance and support.
Evolution and Challenges

The Monroe Doctrine has undergone several revisions and reinterpretations since its initial proclamation.Over time, it has been used to justify both interventionist and non-interventionist policies in Latin America. The most significant challenges to the doctrine have come from the United States’ desire to maintain its influence in the region while respecting the sovereignty of Latin American nations.
The Monroe Doctrine, a policy aimed at preventing European intervention in the Americas, is often depicted on maps. Speaking of maps, have you heard the one about the thirsty cow? Joke: What do cows drink? Moo-juice! Getting back to the Monroe Doctrine, its map serves as a visual representation of this significant policy.
Interventionism and Non-Interventionism
The Monroe Doctrine has been used to justify both interventionist and non-interventionist policies in Latin America. In the early 20th century, the United States intervened in several Latin American countries to protect its economic and strategic interests. However, in the post-World War II era, the United States adopted a more non-interventionist approach, emphasizing respect for the sovereignty of Latin American nations.
Challenges to the Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine has faced several challenges over time. One challenge has been the rise of nationalism in Latin America. Latin American nations have increasingly asserted their independence from the United States and have resisted attempts by the United States to intervene in their affairs.Another
challenge to the Monroe Doctrine has been the emergence of new global powers, such as China and Russia. These powers have sought to increase their influence in Latin America, challenging the United States’ traditional dominance in the region.
Contemporary Relevance
The Monroe Doctrine continues to resonate in the 21st century, shaping US foreign policy towards Latin America. Its core principle of preventing European intervention remains relevant, but its interpretation and application have evolved.
One contemporary implication is the US’s continued commitment to the territorial integrity and political stability of the Western Hemisphere. The doctrine serves as a deterrent against foreign powers seeking to establish influence or control in the region.
US Foreign Policy in the 21st Century
- Prevention of Intervention:The Monroe Doctrine’s legacy ensures that the US remains vigilant against any attempts by external actors to interfere in Latin American affairs.
- Promoting Democracy and Human Rights:The US has used the doctrine to justify interventions aimed at promoting democratic governance and protecting human rights in the region.
- Economic Cooperation:The Monroe Doctrine has fostered economic ties between the US and Latin America, promoting trade and investment while maintaining US influence in the region.
- Challenges to US Dominance:The rise of regional powers like China and Russia has challenged the US’s traditional dominance in Latin America, requiring a reassessment of the Monroe Doctrine’s relevance.
Comparison with Other Doctrines

The Monroe Doctrine shares similarities with other foreign policy doctrines in its objective of protecting American interests in its sphere of influence. However, it differs in its specific scope and approach.
Truman Doctrine
- Both the Monroe Doctrine and the Truman Doctrine aimed to prevent the spread of communism in the Americas.
- However, the Truman Doctrine was more global in scope, applying to all countries threatened by Soviet expansion, while the Monroe Doctrine was limited to the Western Hemisphere.
Bush Doctrine
- The Bush Doctrine, like the Monroe Doctrine, emphasized the use of preemptive military action to protect American interests.
- However, the Bush Doctrine was broader in scope, justifying military interventions in countries that were not posing an immediate threat to the United States, while the Monroe Doctrine focused on preventing European intervention in the Americas.
Maps and Visual Representations
Visual representations can enhance understanding of the Monroe Doctrine’s scope and impact. Maps depict its sphere of influence, while tables summarize key provisions and their effects.
Map of the Monroe Doctrine’s Sphere of Influence
The map below illustrates the extent of the Monroe Doctrine’s influence, encompassing the Americas, excluding European colonies.
[Detailed map of the Monroe Doctrine’s sphere of influence]
Table Summarizing Key Provisions and Impact
The table below summarizes the key provisions of the Monroe Doctrine and their impact on Latin America.
| Provision | Impact |
|---|---|
| No further colonization by European powers | Prevented European powers from establishing new colonies in the Americas |
| Non-intervention by European powers | Protected Latin American nations from European intervention and exploitation |
| Recognition of Latin American independence | Established the United States as a protector of Latin American sovereignty |
FAQ Corner
What was the primary goal of the Monroe Doctrine?
To prevent European powers from interfering in the affairs of the Americas and to assert US dominance in the region.
How did the Monroe Doctrine impact Latin American nations?
It both protected their sovereignty from European intervention and limited their independence by giving the US a pretext for intervention.
What are the key provisions of the Monroe Doctrine?
The US would not interfere in European affairs, and Europe would not interfere in the Americas; any attempt by a European power to colonize or intervene in the Americas would be seen as an act of aggression against the US.