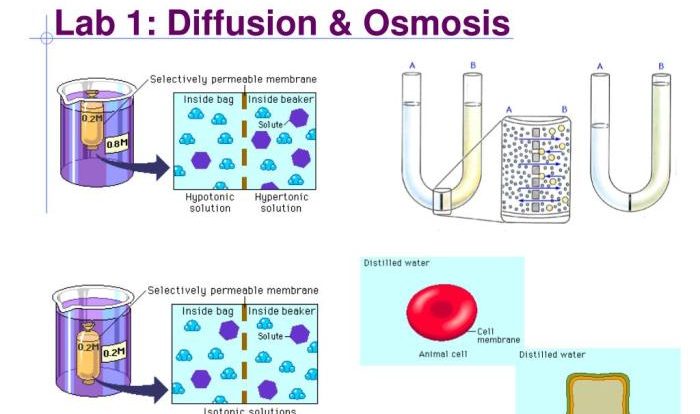
Lab one diffusion and osmosis answers unveil the fundamental principles that govern the movement of molecules and substances across biological membranes. This guide delves into the concepts of diffusion and osmosis, exploring their mechanisms, factors influencing their rates, and their diverse applications in biological systems.
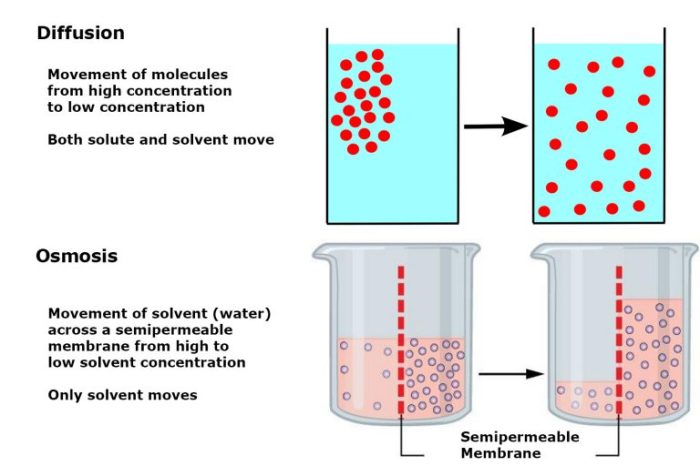
Diffusion, the passive movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to low concentration, plays a crucial role in gas exchange, nutrient transport, and waste removal. Osmosis, on the other hand, involves the selective movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane, driven by concentration gradients of solutes.
Understanding these processes is essential for comprehending numerous physiological and biological phenomena.
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules or ions from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. It is a passive transport process, meaning that it does not require energy input. Diffusion is driven by the concentration gradient, which is the difference in concentration between the two regions.
Factors that Affect the Rate of Diffusion
- Concentration gradient: The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion.
- Temperature: The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion.
- Surface area: The larger the surface area, the faster the rate of diffusion.
- Distance: The shorter the distance between the two regions, the faster the rate of diffusion.
Osmosis
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion that involves the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane is a membrane that allows water molecules to pass through but does not allow other molecules or ions to pass through.
Osmosis is driven by the water potential gradient, which is the difference in water potential between the two regions.
Factors that Affect the Rate of Osmosis
- Water potential gradient: The greater the water potential gradient, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Temperature: The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Surface area: The larger the surface area, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Distance: The shorter the distance between the two regions, the faster the rate of osmosis.
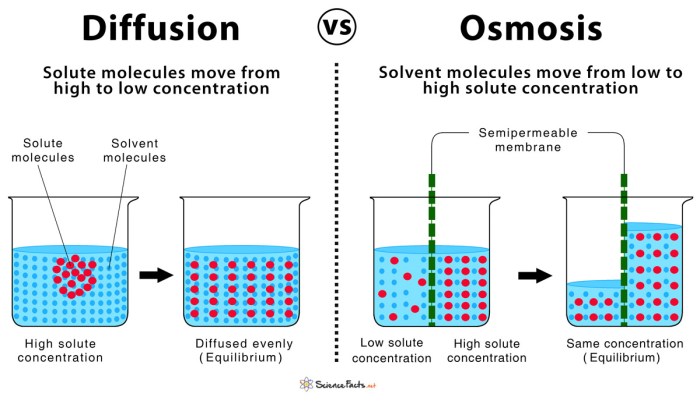
Differences between Diffusion and Osmosis
| Diffusion | Osmosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Movement of molecules or ions from high to low concentration | Movement of water across a semipermeable membrane |
| Mechanism | Passive transport | Passive transport |
| Direction of movement | From high to low concentration | From high to low water potential |
| Examples | Spread of perfume in a room | Water moving from a plant cell to a salt solution |
Applications of Diffusion and Osmosis
Applications of Diffusion in Biological Systems
- Gas exchange in the lungs
- Nutrient absorption in the small intestine
- Waste removal in the kidneys
Applications of Osmosis in Biological Systems
- Water balance in cells
- Turgor pressure in plants
- Dialysis
Experiments to Demonstrate Diffusion and Osmosis: Lab One Diffusion And Osmosis Answers
Experiment to Demonstrate Diffusion
- Place a drop of perfume in the center of a room.
- Wait a few minutes.
- Observe the spread of the perfume.
Experiment to Demonstrate Osmosis
- Place a plant cell in a salt solution.
- Observe the cell over time.
- The cell will shrink as water moves out of the cell.
Real-World Examples of Diffusion and Osmosis
Real-World Examples of Diffusion
- The spread of a virus through a population
- The movement of pollutants in the air
- The diffusion of oxygen into the blood
Real-World Examples of Osmosis, Lab one diffusion and osmosis answers
- The absorption of water by plants
- The movement of water across the placenta
- The use of dialysis to remove waste products from the blood
Query Resolution
What is the primary difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion involves the movement of molecules from high to low concentration, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
What factors influence the rate of diffusion?
Temperature, concentration gradient, surface area, and membrane thickness all affect the rate of diffusion.
How does osmosis contribute to maintaining cell volume?
Osmosis regulates water movement across cell membranes, preventing cells from shrinking or bursting due to changes in solute concentration.