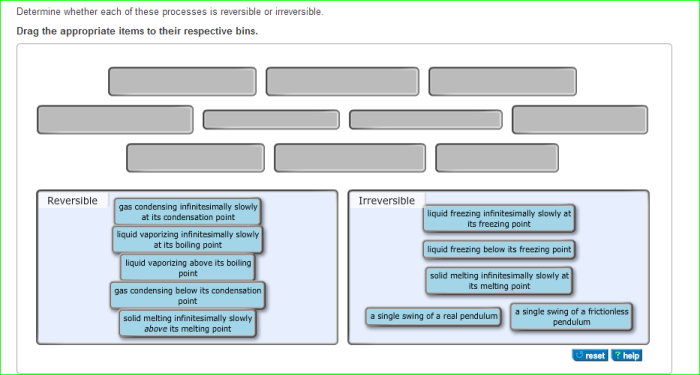
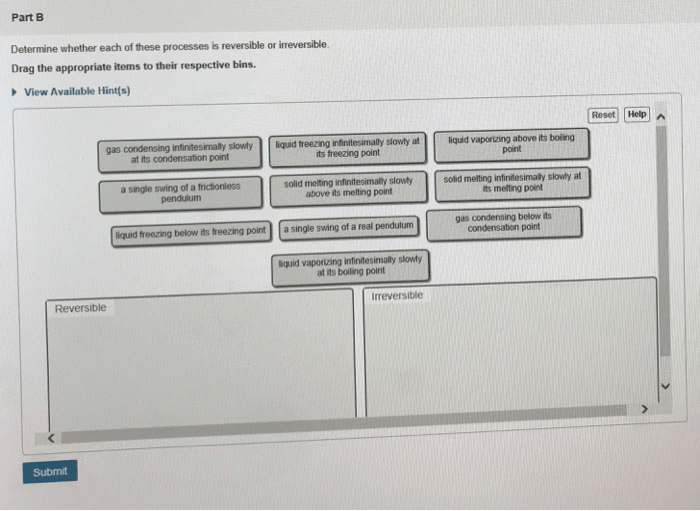
Determine whether each of these processes is reversible or irreversible. – The concept of reversibility plays a pivotal role in understanding the nature of processes. Determining whether a process is reversible or irreversible is crucial for various scientific and engineering applications. This discourse delves into the characteristics, factors, and implications of reversible and irreversible processes, providing a comprehensive analysis of their significance.
Reversible processes are those that can be reversed, returning the system to its initial state without any net change. Irreversible processes, on the other hand, proceed in one direction only, leading to a permanent change in the system.
1. Processes that are Reversible: Determine Whether Each Of These Processes Is Reversible Or Irreversible.
A reversible process is a process that can be reversed, meaning it can be brought back to its original state without any net change in the system. In other words, the system can be returned to its initial state by reversing the direction of the process.
Examples of reversible processes in everyday life include:
- Melting and freezing of water
- Evaporation and condensation of water
- Stretching and releasing of a rubber band
- Compression and expansion of a gas
The characteristics that make a process reversible include:
- The process is carried out at a constant temperature.
- The process is carried out slowly enough that the system is always in equilibrium.
- There is no friction or other irreversible forces acting on the system.
2. Processes that are Irreversible
An irreversible process is a process that cannot be reversed, meaning it cannot be brought back to its original state without a net change in the system. In other words, the system cannot be returned to its initial state by reversing the direction of the process.
Examples of irreversible processes in everyday life include:
- Burning of fuel
- Mixing of two different substances
- Diffusion of a gas
- Heat transfer from a hot object to a cold object
The characteristics that make a process irreversible include:
- The process is carried out at a non-constant temperature.
- The process is carried out too quickly for the system to reach equilibrium.
- There is friction or other irreversible forces acting on the system.
3. Factors Determining Reversibility
The factors that determine whether a process is reversible or irreversible include:
- The nature of the process itself
- The conditions under which the process is carried out
- The presence of external forces
For example, the process of melting ice is reversible if it is carried out at a constant temperature and pressure. However, if the ice is melted by heating it with a flame, the process is irreversible because the heat from the flame causes the ice to melt too quickly and the system does not reach equilibrium.
4. Applications of Reversibility and Irreversibility

Reversible processes are used in a variety of applications, such as:
- Refrigerators and air conditioners
- Heat pumps
- Chemical reactions
- Electrical circuits
Irreversible processes are used in a variety of applications, such as:
- Engines
- Generators
- Friction
- Diffusion
5. Advanced Concepts in Reversibility
Microscopic reversibility is the principle that the microscopic laws of physics are the same in both directions of time.
Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases over time.
Advanced concepts in reversibility are used in a variety of scientific research, such as:
- Statistical mechanics
- Quantum mechanics
- Cosmology
FAQ Resource
What are the key characteristics of reversible processes?
Reversible processes occur at equilibrium, involve no friction or other dissipative forces, and can be reversed without any net change in the system.
How does entropy relate to process reversibility?
Entropy, a measure of disorder, increases in irreversible processes but remains constant in reversible processes.