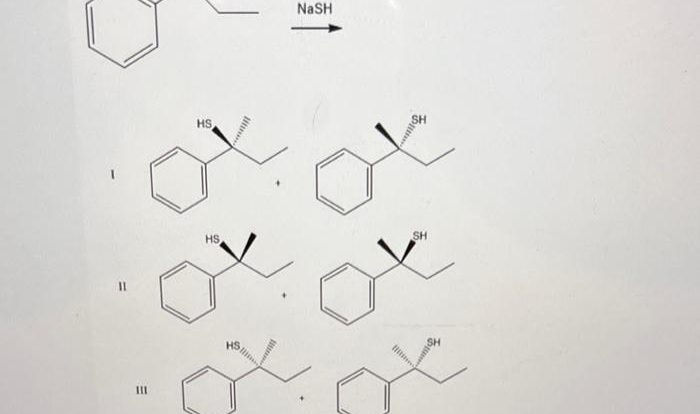
Identify reagents that can be used for the following synthesis – Identifying reagents for chemical synthesis is a crucial step in the successful execution of any synthetic procedure. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the factors to consider when selecting appropriate reagents, including their functional groups, reactivity, and compatibility with the reaction conditions.
By understanding the principles behind reagent selection, chemists can optimize their syntheses, improve yields, and minimize the risk of side reactions.
Reagents Identification
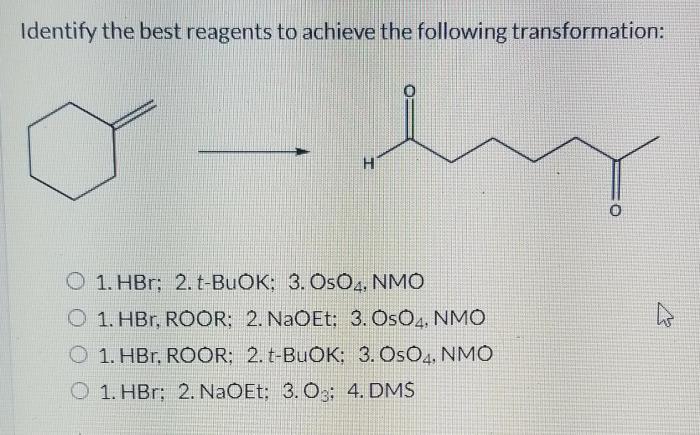
To identify suitable reagents for the synthesis, it is crucial to understand the desired chemical transformation and the functional groups involved. Reagents can be classified based on their functional groups and reactivity, allowing for a systematic selection process. Factors to consider when choosing reagents include their availability, cost, toxicity, and compatibility with the reaction conditions.
Common Functional Groups and Corresponding Reagents
- Alcohols:Grignard reagents, organolithium compounds, alkyl halides
- Aldehydes and Ketones:Nucleophiles (e.g., Grignard reagents, organolithium compounds), reducing agents (e.g., sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride)
- Carboxylic Acids:Acyl chlorides, acid anhydrides, esters, amides
- Amines:Alkyl halides, sulfonyl chlorides, isocyanates
- Alkynes:Hydrogenation catalysts (e.g., Lindlar’s catalyst), hydroboration reagents
Reaction Mechanisms: Identify Reagents That Can Be Used For The Following Synthesis

The reaction mechanisms involved in the synthesis provide a detailed understanding of the chemical transformations that occur. Key steps and intermediates in the process are identified, along with a description of the bond formation and cleavage events.
Example Reaction Mechanism
Consider the nucleophilic addition of a Grignard reagent to a ketone. The mechanism involves the following steps:
- Initiation:The Grignard reagent reacts with the ketone to form a tetrahedral intermediate.
- Addition:The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, forming a new carbon-carbon bond and an alkoxide ion.
- Protonation:The alkoxide ion is protonated by water or another acidic species, yielding the final alcohol product.
Reaction Conditions
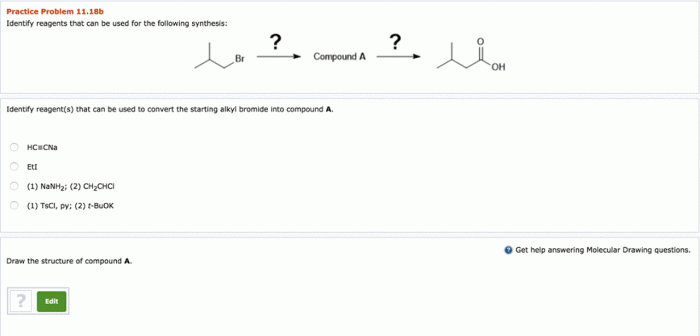
Optimal reaction conditions play a crucial role in the success of the synthesis. Temperature, pressure, solvent, and other parameters influence the reaction rate and yield.
Effects of Reaction Conditions
- Temperature:Higher temperatures generally increase reaction rates, but can also lead to side reactions and decomposition.
- Pressure:Increased pressure can favor reactions involving gases or volatile compounds.
- Solvent:The solvent can affect the solubility of reactants and products, as well as the stability of intermediates.
- Other Parameters:pH, concentration, and the presence of catalysts can also impact reaction conditions.
Product Isolation and Characterization
After the reaction is complete, the product must be isolated and purified. Various methods are employed, depending on the nature of the product.
Isolation Methods, Identify reagents that can be used for the following synthesis
- Extraction:Separating the product from the reaction mixture using a solvent.
- Distillation:Separating volatile compounds based on their boiling points.
- Crystallization:Recrystallizing the product from a suitable solvent to obtain pure crystals.
Characterization Methods
- Spectroscopy (e.g., NMR, IR, UV-Vis):Identifying the functional groups and structure of the product.
- Chromatography (e.g., HPLC, GC):Separating and analyzing mixtures of compounds.
- Melting Point/Boiling Point Determination:Establishing the purity and identity of the product.
Safety Considerations
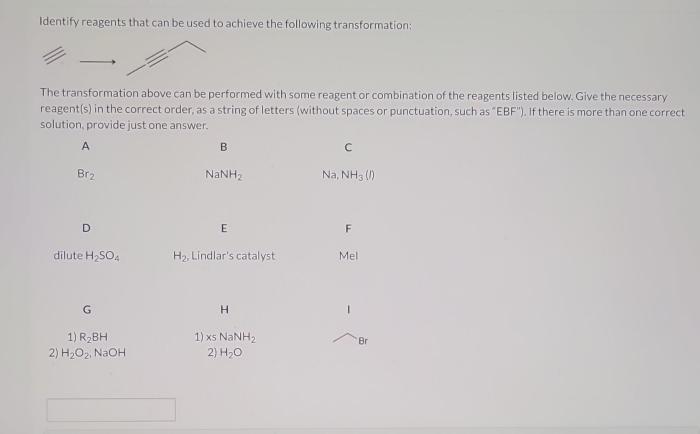
Handling chemicals and reagents in the laboratory requires strict adherence to safety protocols.
Potential Hazards
- Toxic Chemicals:Identifying and mitigating the risks associated with hazardous substances.
- Flammable Materials:Ensuring proper handling and storage of flammable liquids and gases.
- Corrosive Substances:Taking precautions to prevent contact with corrosive acids and bases.
Safety Precautions
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):Wearing appropriate PPE (e.g., gloves, goggles, lab coat) to minimize exposure.
- Proper Ventilation:Ensuring adequate ventilation to remove hazardous fumes and vapors.
- Safe Disposal:Following established protocols for the disposal of chemicals and reagents.
Clarifying Questions
What are the key factors to consider when selecting reagents for chemical synthesis?
The key factors to consider when selecting reagents for chemical synthesis include their functional groups, reactivity, and compatibility with the reaction conditions.
How can I determine the appropriate reagents for a specific reaction?
To determine the appropriate reagents for a specific reaction, consider the functional groups of the starting materials and the desired product, as well as the reaction mechanism and the required reaction conditions.