Design a synthesis of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene from tert-butanol. This article presents a comprehensive overview of the synthesis of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene from tert-butanol, a valuable intermediate in organic chemistry. We delve into the reaction mechanism, optimization strategies, applications, and safety considerations, providing a thorough understanding of this important process.
The synthesis of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene from tert-butanol is a versatile and efficient method for accessing this versatile building block. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the design and execution of this synthesis, empowering chemists with the knowledge to incorporate this valuable intermediate into their research and applications.
Synthesis of 3-Bromo-2-methylpropene from tert-Butanol: Design A Synthesis Of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene From Tert-butanol.
The synthesis of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene from tert-butanol is a versatile and efficient method for the preparation of this valuable building block in organic chemistry. 3-Bromo-2-methylpropene finds wide applications in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and other specialty chemicals.
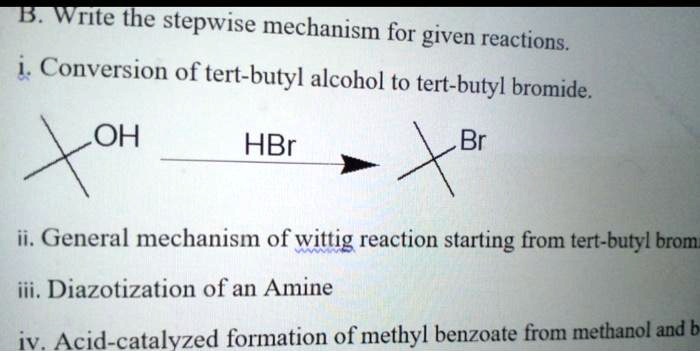
Mechanism of the Synthesis
The synthesis involves a three-step process:
- Protonation of tert-butanol by a strong acid, such as sulfuric acid, to form the tert-butyl cation.
- Rearrangement of the tert-butyl cation to form the more stable isobutyl cation.
- Addition of bromide ion to the isobutyl cation to form 3-bromo-2-methylpropene.
The regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction are controlled by the stability of the carbocations formed during the rearrangement step. The isobutyl cation is more stable than the tert-butyl cation, which drives the rearrangement towards the formation of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene.
Optimization of the Synthesis
The yield and selectivity of the synthesis can be optimized by controlling the reaction parameters:
- Temperature:Lower temperatures favor the formation of the more stable isobutyl cation, resulting in higher selectivity for 3-bromo-2-methylpropene.
- Solvent:Polar solvents, such as water, facilitate the protonation step and enhance the yield of the product.
- Catalyst:The use of a strong acid catalyst, such as sulfuric acid, is crucial for the protonation step and the rearrangement of the carbocations.
Applications of the Synthesis, Design a synthesis of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene from tert-butanol.
3-Bromo-2-methylpropene is a versatile intermediate used in the synthesis of a wide range of compounds, including:
- Pharmaceuticals, such as anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics
- Fragrances, such as linalool and geraniol
- Fine chemicals, such as dyes and pigments
Safety Considerations
The synthesis of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene involves the use of corrosive and toxic reagents. It is essential to follow proper safety protocols:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
- Handle the reagents and products in a well-ventilated area.
- Dispose of the waste products according to the local regulations.
FAQ Overview
What is the importance of 3-bromo-2-methylpropene?
3-Bromo-2-methylpropene is a valuable intermediate in organic synthesis due to its versatility as an electrophile and its ability to participate in a wide range of reactions, including alkylations, cycloadditions, and nucleophilic substitutions.
What are the key factors affecting the yield and selectivity of the synthesis?
The yield and selectivity of the synthesis are influenced by several factors, including the reaction temperature, solvent choice, and the type and amount of catalyst employed. Optimization of these parameters is crucial for achieving high yields of the desired product.
What are the potential hazards associated with the synthesis?
The synthesis involves the use of hazardous chemicals, such as tert-butyl chloride and hydrogen bromide. It is essential to follow proper safety protocols, including the use of appropriate personal protective equipment and adequate ventilation, to minimize the risks associated with handling and disposing of these materials.