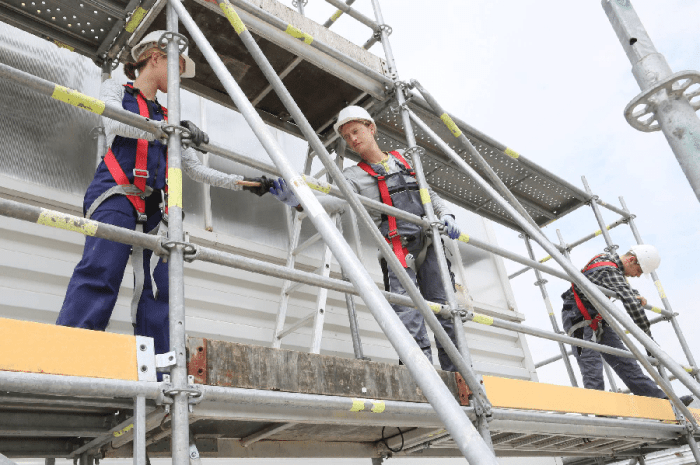
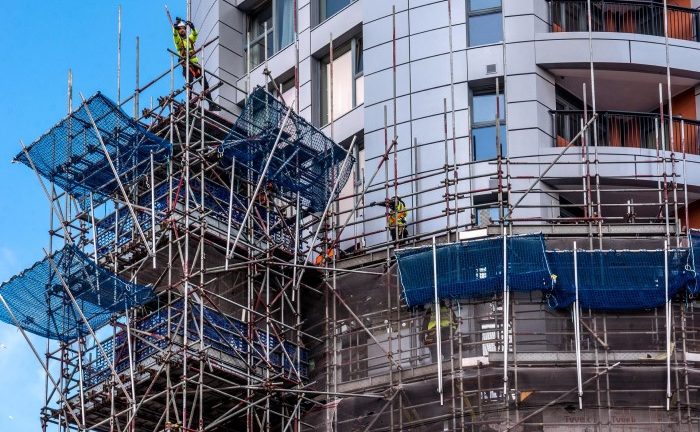
Scaffold accidents are usually attributed to factors like inadequate planning, faulty equipment, unsafe practices, environmental hazards, and insufficient training. Understanding these factors is crucial for preventing such accidents and ensuring worker safety.
Thorough planning, meticulous supervision, high-quality equipment, and comprehensive training are essential pillars of scaffold safety. By addressing these factors, we can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and promote a safe working environment for scaffold workers.
Scaffold Accidents: Causes and Prevention
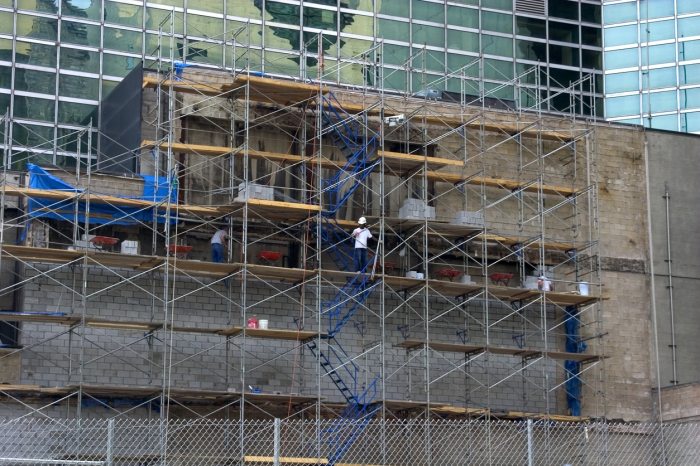

Scaffold accidents are a serious concern in the construction industry, accounting for a significant number of injuries and fatalities. These accidents are often attributed to factors such as inadequate planning and supervision, faulty scaffolding equipment, unsafe work practices, environmental factors, and inadequate training and education.
Inadequate Planning and Supervision
Thorough planning and supervision are essential for preventing scaffold accidents. Proper planning involves assessing the worksite, identifying potential hazards, and developing a comprehensive safety plan. Adequate supervision ensures that the plan is implemented effectively and that workers are following safe work practices.
Poor planning and inadequate supervision can lead to a variety of problems, including:
- Inadequate assessment of worksite hazards
- Improper selection and assembly of scaffolding equipment
- Lack of fall protection measures
- Insufficient training for workers
Faulty Scaffolding Equipment
Using high-quality and well-maintained scaffolding equipment is crucial for worker safety. Scaffolding equipment includes platforms, guardrails, ladders, and braces. Each component must be inspected regularly to ensure it is in good working condition.
Common types of scaffolding equipment failures include:
- Broken or damaged platforms
- Loose or missing guardrails
- Faulty ladders
- Corrosion or rust
Unsafe Work Practices
Unsafe work practices contribute significantly to scaffold accidents. These practices include:
- Overloading scaffolding
- Improper assembly or disassembly
- Working without fall protection
- Ignoring safety regulations
Best practices for safe work on scaffolding include:
- Following the manufacturer’s instructions for assembly and use
- Inspecting scaffolding equipment regularly
- Using fall protection equipment
- Following established safety protocols
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can affect the safety of scaffolding. Wind, rain, and snow can impact scaffold stability and increase the risk of accidents.
Environmental hazards to consider include:
- High winds
- Heavy rain or snow
- Lightning
- Icy conditions
Training and Education, Scaffold accidents are usually attributed to factors like
Proper training and education for scaffold workers are essential for preventing accidents. Workers should receive training on:
- Basic safety principles
- Advanced scaffolding techniques
- Rescue procedures
Effective training programs can reduce the risk of scaffold accidents by ensuring that workers have the knowledge and skills to work safely on scaffolding.
Q&A: Scaffold Accidents Are Usually Attributed To Factors Like
What are the most common factors contributing to scaffold accidents?
Inadequate planning, faulty equipment, unsafe work practices, environmental hazards, and insufficient training are the primary factors.
How can we prevent scaffold accidents?
By implementing thorough planning, meticulous supervision, using high-quality equipment, enforcing safe work practices, mitigating environmental hazards, and providing comprehensive training.
What are the best practices for working safely on scaffolding?
Always wear proper safety gear, inspect the scaffold before use, follow assembly instructions, avoid overloading, and never work in adverse weather conditions.