Diffusion and Osmosis Lab AP Biology: Unveiling the Mechanisms of Molecular Transport
Diffusion and osmosis are fundamental processes that underpin countless biological phenomena. This laboratory investigation delves into the intricacies of these processes, exploring their mechanisms, applications, and significance in living systems.
Diffusion: Diffusion And Osmosis Lab Ap Biology

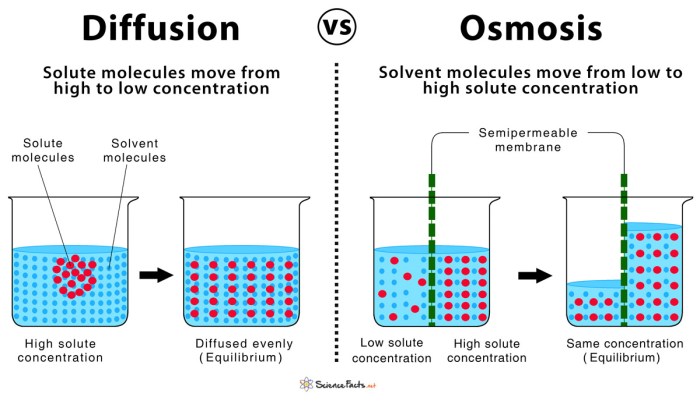
Diffusion is a fundamental process in biology that involves the movement of molecules or particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It is driven by the random motion of molecules and the tendency for molecules to spread out evenly in space.
Diffusion plays a crucial role in various biological systems, including nutrient transport, waste removal, and gas exchange.Examples of diffusion in living organisms include the movement of oxygen from the lungs to the blood, the movement of carbon dioxide from the blood to the lungs, and the movement of nutrients from the small intestine to the bloodstream.The
rate of diffusion is affected by several factors, including the concentration gradient (the difference in concentration between the two areas), the temperature, the size of the molecules, and the presence of barriers. Higher concentration gradients, higher temperatures, and smaller molecules lead to faster diffusion rates.
Barriers, such as cell membranes, can slow down diffusion.
Osmosis
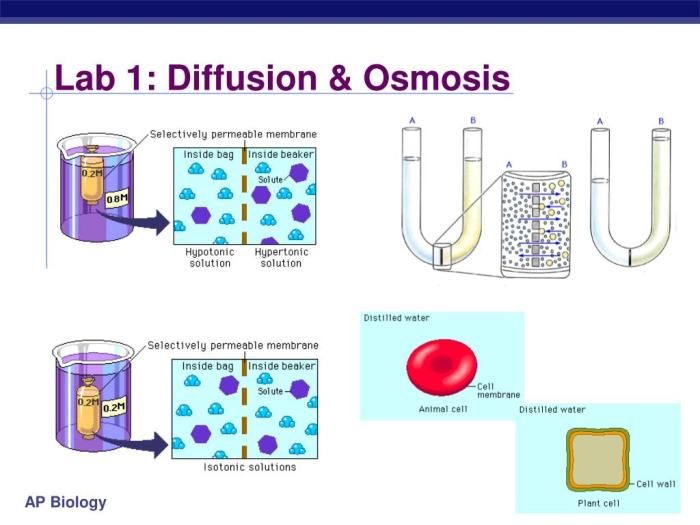
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane is a membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through while blocking others. In osmosis, water molecules move from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration).The
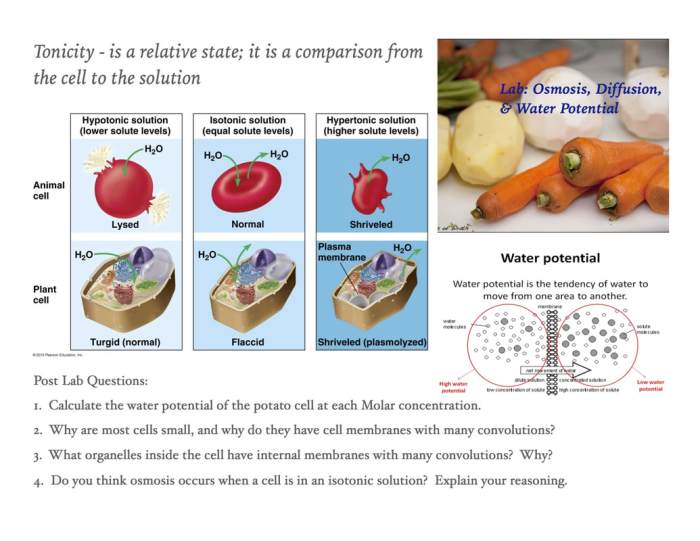
role of semipermeable membranes in osmosis is crucial because it allows for the selective movement of water molecules. This process is essential for maintaining water balance in cells and tissues. For example, if a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (a solution with a higher solute concentration than the cell), water will move out of the cell, causing it to shrink.
Conversely, if a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution (a solution with a lower solute concentration than the cell), water will move into the cell, causing it to swell.
Diffusion and Osmosis Lab
*Experiment to Demonstrate Diffusion and Osmosis
Materials:* Two beakers
- Water
- Sugar
- Semipermeable membrane (e.g., dialysis tubing)
- Graduated cylinder
- Ruler
Procedure:
- Fill one beaker with pure water and the other beaker with a sugar solution.
- Place the semipermeable membrane in the beaker with the sugar solution.
- Tie off one end of the membrane and fill it with water.
- Measure the initial height of the water level in the membrane.
- Place the membrane in the beaker with the sugar solution.
- Observe the changes in the water level in the membrane over time.
Results:Over time, the water level in the membrane will decrease, indicating that water molecules are moving from the water side to the sugar solution side. This is because the sugar solution has a higher solute concentration than the water, creating a concentration gradient for water molecules.Conclusion:The
results of this experiment support the concepts of diffusion and osmosis. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, and osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
Applications of Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis have numerous practical applications in various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and industry.Medicine:*
-*Drug delivery
Diffusion is used to deliver drugs to specific tissues or organs in the body.
-*Dialysis
Osmosis is used in dialysis machines to remove waste products from the blood of patients with kidney failure.
Agriculture:*
-*Fertilization
Diffusion is used to deliver nutrients to plants through fertilizers.
-*Irrigation
Osmosis is used to control the water balance in plants by regulating the flow of water through their roots.
Industry:*
-*Water purification
Osmosis is used in reverse osmosis systems to remove impurities from water.
-*Food processing
Diffusion is used to preserve food by removing moisture.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of diffusion and osmosis. These processes play a vital role in various aspects of our lives, from maintaining the health of our bodies to providing us with the food we eat.
FAQ Explained
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to low water concentration.
What factors affect the rate of diffusion?
Temperature, concentration gradient, surface area, and membrane thickness.
What is the role of semipermeable membranes in osmosis?
Semipermeable membranes allow water molecules to pass through but restrict the passage of solutes, creating a concentration gradient that drives osmosis.